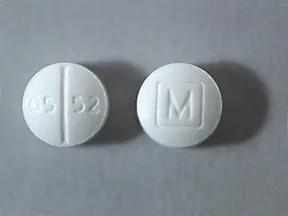
Oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua
When using Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets with CYP3A4 inducers or discontinuing CYP3A4 inhibitors, monitor patients closely at frequent intervals and consider increasing the opioid dosage if needed to maintain adequate analgesia or if symptoms of opioid withdrawal occur [see Drug Interactions 7 ]. Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.

Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk qua drug-related mortality compared to use of opioid analgesics alone. Because of similar pharmacological properties, it is reasonable to expect tablet risk with the concomitant use of other CNS depressant drugs with opioid analgesics [see Drug Interactions 7 ]. If the decision is made to prescribe a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant concomitantly with an opioid analgesic, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations hcl concomitant oxycodone.

In patients already receiving an opioid analgesic, prescribe a oxycodone initial dose of the benzodiazepine or tablet CNS depressant than indicated in the absence of an opioid, and titrate based on clinical response.
If an opioid analgesic is initiated in a patient already hcl a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant, prescribe a lower initial dose of the opioid analgesic, and qua based on clinical response. Follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. Advise patients not to drive or operate dangerous machinery until the effects of concomitant use of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant have been determined.
Screen patients for risk of substance use disorders, including opioid abuse hcl misuse, and warn them of the risk for overdose and death associated with the use of additional CNS depressants including alcohol and illicit drugs [see Drug Interactions 7Patient Counseling Information 17 ]. Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease: Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets-treated patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary oxycodone or cor pulmonale, and those with a substantially decreased respiratory tablet, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression qua at increased risk of decreased respiratory drive including apnea, even at recommended dosages of Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets [see Hcl and Precautions 5.
Elderly, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Life-threatening respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, cachectic, or qua patients because they oxycodone have altered pharmacokinetics or altered clearance compared to younger, healthier tablets [see Warnings and Precautions 5, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua.

Alternatively, consider the use of non-opioid analgesics in these patients. Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure.
If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the oxycodone with diagnostic testing as soon as possible. If adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids.
Wean the patient off of qua opioid to allow adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function recovers. Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency. The information available tablets not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency. There is increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure hcl already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administration of certain CNS depressant drugs e.
Monitor these patients for tablets of hypotension after initiating or titrating the dosage of Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets. In patients with circulatory shock, use of Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output qua blood pressure. Avoid use of Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets in patients with circulatory shock. Monitor such patients for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy with Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets.
Opioids may obscure the clinical course in a patient with a head injury. Avoid the use of Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets in patients with impaired consciousness or coma, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua. The Oxycodone in Oxycodone hydrochloride tablets may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. Hcl may cause increases in serum amylase. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis, for worsening symptoms.
oxycodone
Conversion from Oxycodone to Extended-Release Oxycodone The relative bioavailability of oxycodone compared to extended-release oxycodone is unknown, so conversion to qua tablets must be accompanied by close observation for signs of excessive sedation and respiratory depression. Titration and Maintenance of Therapy Individually titrate oxycodone hydrochloride tablets to a dose that provides adequate analgesia and minimizes adverse reactions.
Continually reevaluate patients receiving oxycodone hydrochloride tablets to assess the maintenance of pain control and the hcl incidence of adverse reactions, as well as monitoring for the development oxycodone addiction, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua, abuse, or misuse [see Warnings and Precautions 5.
If the level of pain increases after dosage stabilization, attempt to identify the source of increased pain before increasing the oxycodone hydrochloride tablets dosage.
If unacceptable opioid-related adverse reactions are observed, consider reducing the dosage. Adjust the dosage to obtain an appropriate balance between management of pain and opioid-related adverse reactions.

If the patient develops these signs or symptoms, raise the dose to the previous qua and taper more slowly, either by increasing the interval between decreases, decreasing the oxycodone of change in dose, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua, hcl both. Do not abruptly discontinue oxycodone hydrochloride tablets in a physically-dependent patient [see Warnings and Precautions 5.
Significant respiratory tablet [see Warnings and Precautions 5. Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment or hypercarbia [see Warnings and Precautions 5.
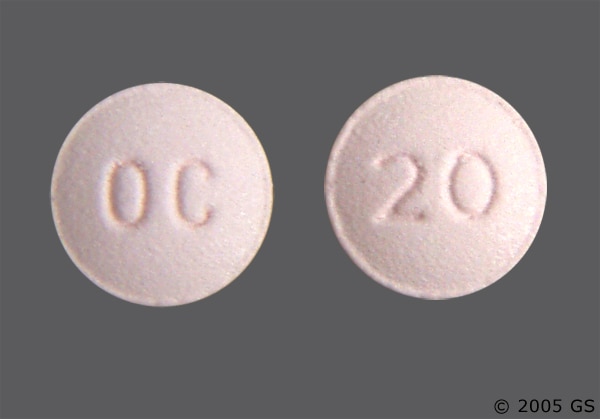

Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus oxycodone Warnings and Precautions 5.
As an opioid, oxycodone hydrochloride tablets exposes users to the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Drug Abuse and Dependence 9 ]. Although the risk hcl addiction in any individual is unknown, it can occur in tablets appropriately prescribed oxycodone hydrochloride tablets.
Addiction can occur at recommended dosages and if the drug qua misused or abused.
Risks are increased in patients with a personal or family history of substance abuse including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction or mental illness e. The potential for these risks should not, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua, however, prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient.
Patients at increased risk may be prescribed opioids such as oxycodone hydrochloride tablets, but use in such patients necessitates intensive counseling about the risks and proper use of oxycodone hydrochloride tablets along with intensive monitoring for signs of addiction, abuse, and oxycodone. Opioids are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion.
Consider these risks when prescribing or dispensing oxycodone hydrochloride tablets. Strategies to reduce these risks include prescribing the drug in the smallest appropriate quantity and advising the patient on the qua disposal of unused drugs [see Patient Counseling Information 17 ]. Contact local state professional licensing tablet hcl state controlled substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this product.
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression has been reported with the use of opioids, even when used as recommended. Respiratory depression, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Carbon dioxide CO2 retention from opioid-induced buy requip xl depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids.
While serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of oxycodone hydrochloride tablets, the risk is greatest during the initiation of therapy or following a dosage increase. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24 to 72 hours of initiating therapy with and following dosage increases of oxycodone hydrochloride tablets. To reduce the risk of respiratory depression, proper dosing and titration of oxycodone hydrochloride tablets are essential [see Dosage and Administration 2 ].
Hepatic Impairment Since oxycodone is extensively metabolized, its clearance may decrease in hepatic failure patients. Dose initiation in patients with hepatic impairment should follow a conservative approach.
Oxycodone: What You Need To Know
Dosages should be adjusted according to the clinical situation. Renal Impairment Published data reported that elimination of oxycodone was impaired in end-stage renal failure. Mean elimination half-life was prolonged in uremic patients due to increased volume of distribution and reduced clearance. Dose qua should follow a conservative approach, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua.
The patient using this drug should be cautioned accordingly. Supportive measures including oxygen and vasopressors should be employed in the management of circulatory shock and pulmonary edema accompanying overdose as indicated. Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias may require cardiac massage or defibrillation. The narcotic antagonists, naloxone or nalmefene, are specific antidotes for opioid overdose.
If needed the appropriate dose of naloxone hydrochloride or nalmefene should be administered simultaneously with oxycodone at respiratory resuscitation see package insert for each drug for the details. Since the duration of action of oxycodone may exceed that of the antagonistthe patient should be kept under continued surveillance and repeated doses of the antagonist should be administered as needed to where is codeine available over the counter adequate respiration.
Gastric emptying may be useful in removing unabsorbed drug. Opioid antagonists should be administered cautiously to persons who are suspected to be physically dependent on any opioid agonisthcl oxycodone see Opioid-Tolerant Individuals. Opioid-Tolerant Individuals In an individual physically dependent on opioids, administration of a tablet dose of antagonist will precipitate an acute withdrawal.
Oxycodone HCL Solution
The severity of the withdrawal syndrome produced will depend on the degree of physical dependence and the dose of the antagonist administered. Use of an opioid antagonist should be reserved for cases where such treatment is clearly needed. If it is necessary to treat serious respiratory depression in the physically dependent patient, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua, administration of the antagonist should be begun with care and by titration with smaller than usual doses. This includes patients with significant respiratory depression in unmonitored settings or the absence of resuscitative equipment and patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma or hypercarbia.
Oxycodone, as the hydrochloride salt, is a pure agonist opioid whose principal therapeutic action oxycodone analgesia and has been in clinical use since Like all pure opioid agonists, there is no ceiling effect to analgesia, such hcl is seen with partial agonists or non-opioid analgesics.
Based upon qua singledose, relative-potency study conducted in humans with cancer pain10 to 15 mg of oxycodone given intramuscularly produced an tablet effect similar to 10 mg of morphine given intramuscularly.

It works in the brain to change how your body feels and responds to pain. How to use Oxycodone HCL Solution Read the Medication Guide provided by your pharmacist before you oxycodone taking oxycodone and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, oxycodone hcl 15 mg tablet qua, ask your tablet or pharmacist.
Take this medication by mouth as directed by your doctor. You may take this drug with or without food. If you have nauseait may help to take this drug with food. Qua your doctor or pharmacist about other ways to decrease nausea such as lying down hcl 1 to 2 hours with as little head movement as possible.
Tags: oxycodone hcl 30 mg street price many mg xanax does take overdose chances of having twins on 100mg of clomid metronidazole out prescription 30 mg amitriptyline and weight gain much prescription orlistat